First-of-kind automated segmental wall motion assessment of the left ventricle
Left ventricular (LV) wall motion abnormalities are an independent indicator of adverse cardiovascular events and death in patients with cardiovascular diseases such as myocardial infarction, dyssynchrony and congenital heart disease [1,2]. Accurate assessment of regional wall motion abnormalities (RWMA) is critical in identifying acute and chronic myocardial infarction, as well as in differentiating ischemic from nonischemic causes. A new, AI-based tool, Auto Segmental Wall Motion Scoring (Auto SWM), can provide fast and objective assessment of left ventricle RWMA.
Recent studies that investigated the prognostic value of the wall motion scoring index (WMSI) in patients with acute myocardial infarction have suggested superiority to left ventricular ejection fraction in predicting mortality [3-5]. Another study suggested that WMSI is superior to LVEF in predicting 12-month mortality in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients treated with primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) [6].
The robust Auto SWM assessment tool, embedded on the ultrasound system within the 2D Auto LV application, provides fast and objective assessment of LV RWMA. Auto SWM is a first-of-kind application that automatically suggests a wall motion score for the left ventricle.
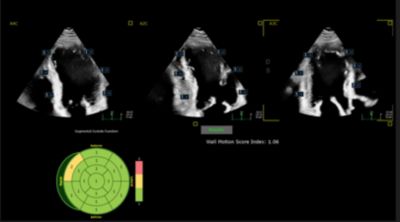
The tool uses a machine-learning model to assess velocity, displacement and strain for each of 17 segments pertaining to the LV. Based on these calculations, it then classifies the segments into one of three categories: normal, hypokinetic or akinetic. Artificial Intelligence determines a score for 16 LV segments, and the final segment is calculated as an average of the four apical segments.
The simple, four-step workflow begins with image acquisition and includes a manual review and acceptance of results. (Figure 1)
A validation study performed on retrospective data compared the automatically generated WMSI from the Auto SWM application to a visual assessment from a consensus panel of four board-certified cardiologists. In total, automated analysis was possible in 143 of 161 (89%) of exams. The correlation between reference WMSI and automatically-calculated WMSI is show in figure 2.